Table of Contents
Analytical constant of fats and oils
1. Acid value
It is defined as number of milligrams of KOH required to neutralize 1gm of fats or oils. It measures the free fatty acids found in oils and fats. Fats and oils contain free fatty acids, which are harmful to humans.
Procedure for acid value
1. Weight accurately quantity of fat and oil in a conical flask.
2. Then added 50ml of ethanol ether solution then shake it well.
3. Titrate the solution with KOH using phenolphthalein as an indicator until pink color is obtained.
4. Then measure the amount of KOH used and calculate the acid value as-
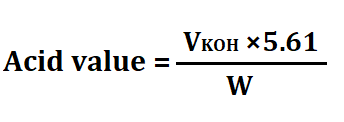
Significance of acid value
1. The value is a measure of the amount of free fatty acid which have been liberated by hydrolysis from the glycerides due to action of moisture, temperature or lipolytic enzyme lipase.
2. Therefore, oils with increased acid number are unsafe for human.
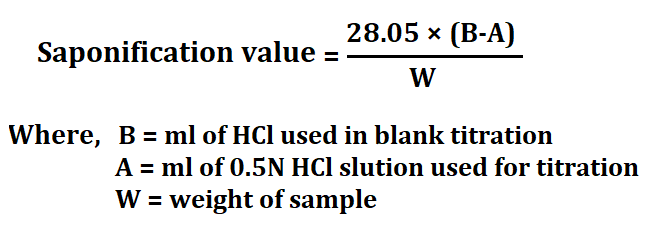
2. Saponification value
This value is defined as the number of mg of NaOH required or KOH required to convert 1 gm of fat completely into soap.
Procedure for saponification value
1. Take 2gm of sample in a conical flask fitted with reflex condenser.
2. Add 25ml of 0.5N ethanolic KOH and boil under reflex on a water bath for 30 minutes.
3. Add 1ml of phenolphthalein solution and titrate with 0.5N HCl solution.
Significance of saponification value
The magnitude of saponification value gives on idea about average molecular weight of the oils and fats. According to this rule, saponification value of reversible proportional is molecular weight.
3. Ester value
Ester value is defined as the number of mg of KOH required to react with the ester in 1gm of fat/oil and to break down into glycerol and fatty acid. It is also defined as difference between saponification value and acid value.

Procedure for ester value
1. Weigh accurately about 2g of sample add 25ml of 0.5M ethanolic acid.
2. Then, boiled under reflex condensing on a water bath for 1 hour.
3. Then, add 20ml of water in it.
4. Then, titrate the excess of alkali with 0.5M HCl using a further 0.2ml of phenolphthalein.
5. Repeat the operation without sample.
Significance of ester value
The ester value shouts the amount alkali consumed in the saponification of the ester and as possible identify and differentiate the fats with this value.
4. Iodine value
Iodine value is defined as the no. of grams of iodine is required to convert 100gm of unsaturated fats into saturated fats. I2 reacts with the π bond and convert them into sigma bond.
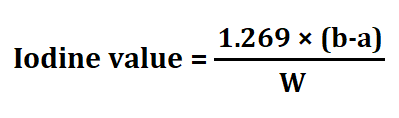
Procedure for iodine value
1. Iodine monochloride solution in glacial acetic acid is used to treat the oil/fat sample taken with carbon tetrachloride.
2. The excess of iodine monochloride is treated with potassium iodine.
3. Now, this sample is titrated against 0.1M sodium thiosulphate solution and this solution used as indicator for estimation of liberated iodine.
4. Then perform a black titration.
Significance of iodine value
The iodine value is a measure of the amount of double bonds in a fat. Unsaturated lipid is more susceptible to rancidity.
5. Acetyl value
It is defined as the total number of mg of KOH required to neutralize acetic acid produced by the saponification of 1gm of fat/oil.
Procedure for acetyl value
1. It is determined through saponification value.
2. Boil the 10gm of sample with 20ml of acetic anhydride for 2 hours.
3. Add 100ml water and boil for 30 minutes.
4. Separate and wash the acetylated product.
5. Determine the saponification value of the acetylated substance(b ml).
6. Determine the saponification value of the substance(a ml).
Significance of acetyl value
The main significance of acetyl value is to determine to number of alcoholic group present in fat/oil.
6. R.M value(Reicher meissi)
It is defined as the number of ml of 0.1N KOH solution required to neutralize the H20 soluble steam or 5gm of hydrolyzed fat/oil sample. It is an inductor of how much volatile fatty acids can be extracted from fat through saponification.

Significance of R.M value
The main significance of R.M value is to determine the purity of fat/oil and natural ghee. Which may contain high number of glycerides salt & butyric acid.



We at present don’t very own an automobile yet whenever I purchase it in future it’ll definitely certainly be a Ford design!