Table of Contents
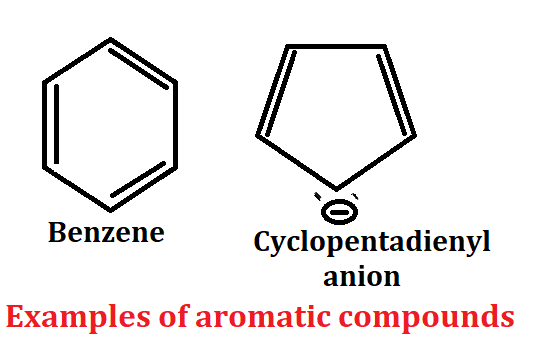
Criteria for aromaticity
1. Aromatic compound present in cyclic system according to criteria for aromaticity.
2. Aromatic compound should be planar. In this compound all atom should have sp2 hybridized mainly.
3. Conjugation of aromatic compound should be complete.
4. Aromatic compound should follow Huckel’s rule according to the criteria of aromaticity.
Huckel’s rule:- The ring system must contain (4n+2)π the electrons used in delocalization (including a single pair if needed), where n is integer = 0, 1, 2,….etc
Examples of aromatic compound
If we talk about benzene then benzene has 6π electron, benzene has also cyclic system, also conjugate system so it is aromatic compound because all the criteria that a compound needs to show aromaticity is all that benzene.
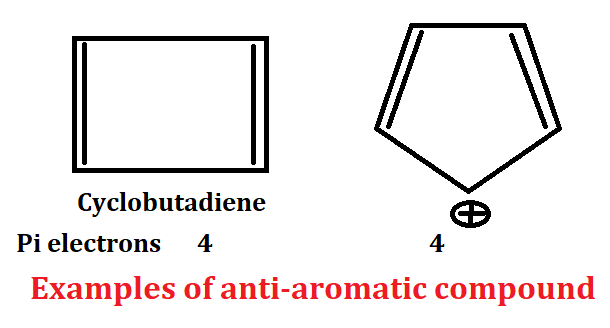
Criteria for anti-aromaticity
1. Anti-aromatic compound present in cyclic system or ring system.
2. Anti-aromatic compound should be planar. In this compound all atom should have sp2 hybridized mainly.
3. Conjugation of anti-aromatic compound should be complete.
4. Planar, cyclic, conjugated species which have 4nπ electron are called anti-aromatic compound.
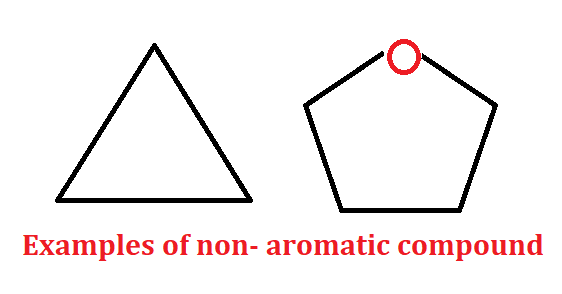
Non-aromatic compound:- The compound other than aromatic and anti-aromatic are non-aromatic compounds.
Benzene
The main member of the aromatic hydrocarbon family is a benzene whose molecular formula is C6H6. It has a hexagonal ring of six carbon atoms with three double bonds in an alternative position. In which benzene has 6 π electrons. Benzene was first obtained by Michael Faraday in 1825.
Preparation of benzene
From sodium benzoate
To obtain benzene from sodium benzoate, sodium benzoate is reacted with soda lime (NaOH and CaO), due to this reaction we easily get benzene and sodium carbonate.

From phenol
Phenol is an aromatic organic compound whose molecular formula is C6H5OH. It has a hexagonal ring of six carbon, five hydrogen and hydroxide with three double bonds. To obtain benzene from phenol, phenol is reacted with zinc dust, which readily gives benzene and zinc oxide.
From chlorobenzene
Chlorobenzene is an aromatic compound whose molecular formula is C6H5Cl. It has a hexagonal ring of six carbon, five hydrogen and chloride with three double bonds in an alternative position. chlorobenzene is reduced from chlorobenzene to yield benzene, in which NaOH is used as a catalyst to give benzene and hydrochloric acid.

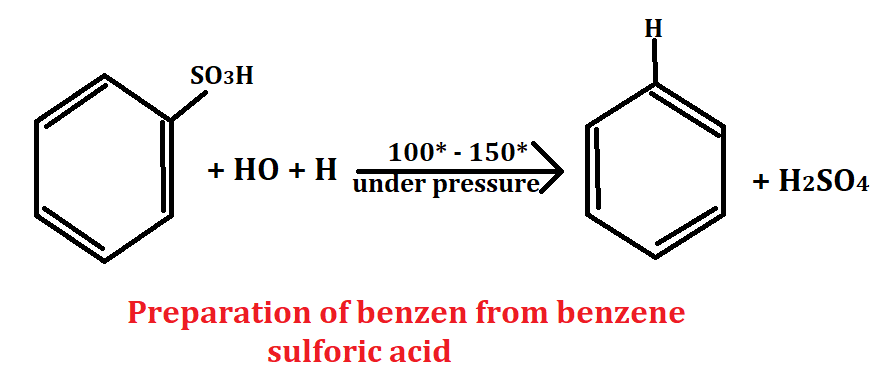
From benzene sulfonic acid
Benzene sulfonic acid is an aromatic compound whose molecular formula is C6H5O3S. To obtain benzene from benzene sulfonic acid, benzene sulfonic acid is reacted with water to yield benzene and sulfuric acid. The sulfuric acid is then removed from benzene with the help of desulphonation.


To the mimprovement.com admin, Thanks for the valuable information!