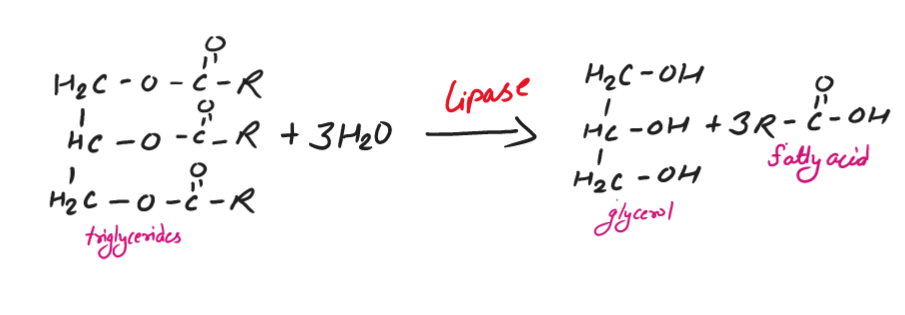Table of Contents
Fats and oils
Fats and oils belong to the natural occurring group of compounds called lipids. All fats and oils are belonged to lipids but all lipids are not fats and oils. Fats and oils are esters, it is able to saponify. Natural fats and oils are the pi-esters of glycerol with long chain carboxylic acid (basically from 12-20 carbons), these are known as triglycerides.
Fats and oils are important sources of energy and nutrients. They are also essential for the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins. Fats and oils can be used to make soap, margarine, salad dressings, mayonnaise, chocolate spreads and other foods that contain a high percentage of fat.
Difference between fats and oils
| Fats | Oils |
| 1. Fats are solid at room temperature. | 1. Oils are liquid at room temperature. |
| 2. Fats are saturated. | 2. Oils are unsaturated. |
| 3. Fats are found in animals. | 3. Oils are found in both animals and plants. |
| 4. Fats are more stable. | 4. Oils are less stable. |
| 5. Fats don’t contain double or triple bond. | 5. Oils contain double and triple bond. |
1. Fats are solid at room temperature but oils are liquid at room temperature.
2. Fats are saturated but oils are unsaturated.
3. Fats are found in animals but oils are found in both animal and plants.
4. Fats are melted at high temperature but oils are melted at low temperature.
5. Fats don’t contain double or triple bond but oils contain double and triple bond.
6. Fats are more stable than oils.
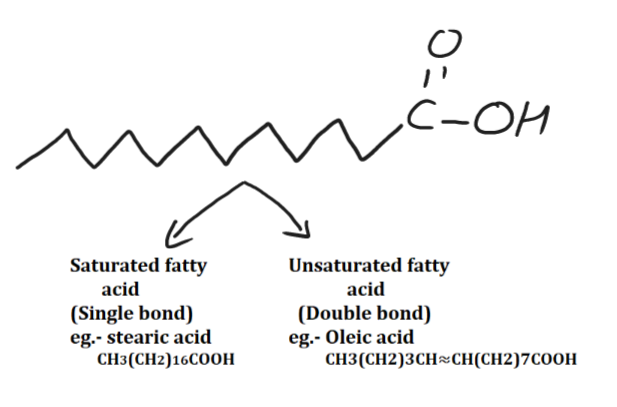
Fatty acid
Long chain of carboxylic acid is known as fatty acids. Fatty acids are organic compounds that are important for many functions in the human body, including energy production and use, cell signaling and immune response. Example- CH3(CH2)10COOH.
There are two types of fatty acids: saturated and unsaturated Fatty acid. Saturated fatty acids have single bond, like stearic acid. Unsaturated fatty acids have double bond, like oleic acid.
Unsaturated fatty acids come into two forms: mono-unsaturated and poly-unsaturated. unsaturated fats can be found mostly in plants. Examples of foods rich in unsaturated fats include vegetable oils such as olive oil or sunflower oil; some nuts such as walnuts or almonds; avocados; soybeans; and certain fish such as salmon or trout.
Glycerol
Glycerol is a type of alcohol that is found in many plants and animals. Glycerol is also a sweet-tasting, colorless liquid that has a chemical formula of C3H8O3. It is often used as an additive to food products such as ice cream, chocolate, and yogurt. Glycerol can also be found in the form of a sweetener called glycerin or glycerin.
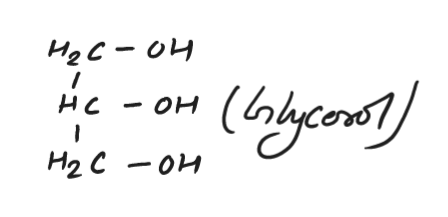
Lipid
Lipids are naturally occurring molecules that can be found in all living organisms. They are not just a part of cell membranes; they also serve as major components of the diet and act as signaling molecules.

Lipids are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents such as ether and chloroform. Lipids are an important class of biological molecules that play a number of critical roles in living organisms. Lipids may also function to insulate tissue from environmental extremes such as heat or cold.
Fatty acid reactions
1. Hydrolysis
In this reaction, triglycerides (tri-esters) are easily hydrolyzed by enzyme called lipase (catalyst) in the digestive tract of animals to give fatty acids and glycerol.
So, the fatty acids produced play an important role in the metabolic process in the animal body.
2. Hydrogenation
The addition of hydrogen in fats and oils in the presence of metal catalyst Ni/Pd/Pt is called hydrogenation reaction.
Unsaturated glycerides react with hydrogen in the presence of a metal catalyst to give saturated glycerides. Vegetables oils are triglycerides of unsaturated fatty acid such as oleic acid and after reaction it form saturated glycerides with in solid form. It is also used for manufacturing of vegetable ghee.
3. Rancidity of oils (Rancidification)
When fats and oils are left exposed to most air and H2O then it will decompose and produce an unpleasant smell and taste become bitter, these fats called Rancidification.
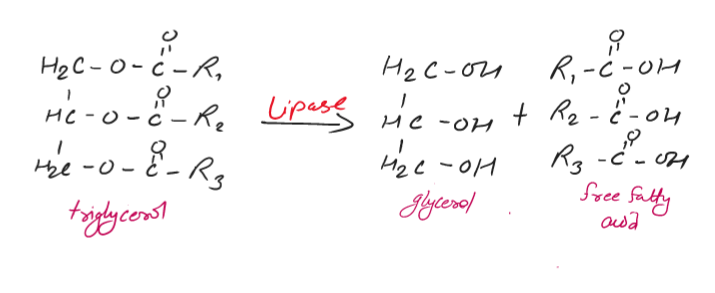
It occurred when fats and oil exposed for any length of time rancidity is by hydrolysis of the ester and oxidation of double bond of the triglycerides.
4. Drying oils
Unsaturated fatty acids/oils absorb oxygen from environment and get polymeric to form a hard transparent coating, this phenomenon is called drying. Those oils which undergo drying is called drying oil.
Eg.- linseed oil (which is rich in linolenic acid) is a common drying oil used in oil-based points.