Table of Contents
Naphthalene
Naphthalene is a colorless, crystalline solid with a strong odor. It is the organic compound with the formula C10H8. Naphthalene is used in mothballs and as an insecticide. Naphthalene was first synthesized by the German chemist Justus von Liebig in 1835.
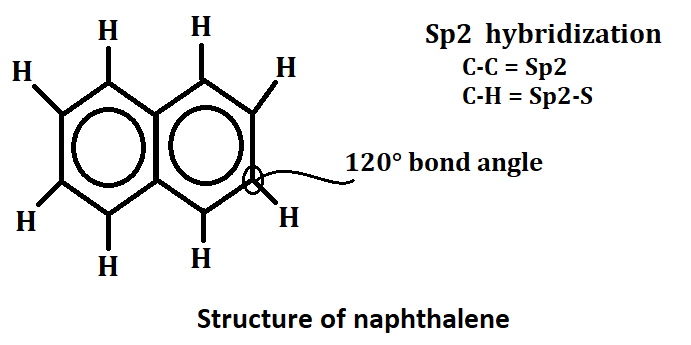
Structure of naphthalene
Naphthalene is a white crystalline hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C10H8. It is composed of two fused benzene rings, and its structure can be represented in three different ways: line-angle formula, condensed formula, and structural formula. Naphthalene has Sp2 hybridized and in this carbon to carbon Sp2 hybridized and carbon to hydrogen Sp2-S hybridized. The bond angle of naphthalene is 120*.
Resonance of naphthalene
According to the resonance theory, naphthalene is considered to be hybrid of three form. Naphthol’s is less aromatic(more reactive) then benzene.
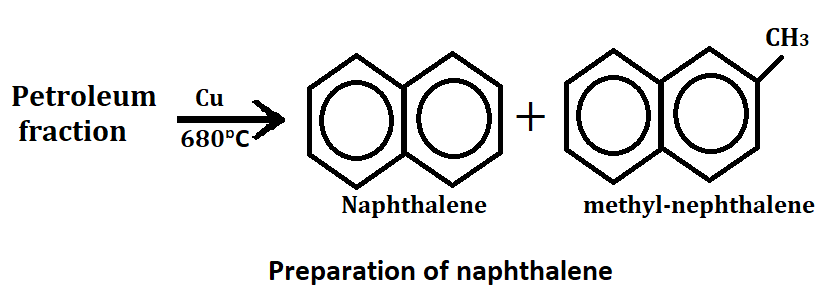
Synthesis of naphthalene
1. From petroleum
When petroleum fraction is passed over copper(Cu) as a catalyst at 680°C then naphthalene and methyl naphthalene are formed.
After this, methyl naphthalene is separated and further converted into naphthalene by heating with hydrogen under process.
2. From 4-phenyl-1-butene
When 4-phenyl-1-butene is react with red hot calcium oxide, then naphthalene is formed.

3. From 4-phenyl-3-butenoic acid
When 4-phenyl-3-butenoic acid is heated with concentration sulfuric acid(H2SO4) then 1 naphthol is formed after that it react with zinc dust then naphthalene produced.
4. By Howarth synthesis
This synthesis of complete in five steps:-
1. Friedel craft acylation:- benzene and succinic anhydride are heated in the presence of aluminum chloride to form B- benzoyl propionic acid.
2. B- benzoyl propionic acid is treated with amalgamated zinc in the presence of hydrochloric acid(HCl) to give ¥-phenyl butyric acid.
3. γ-phenyl butyric acid is heated with concentration H2SO4 or polyphosphoric acid to form α-tetralone.
4. ¢-tetralone is heated with amalgamated zinc and hydrochloric acid to give tetralene.
5. Tetralene is heated with palladium to yield naphthalene.
Physical properties of naphthalene
1. It is a colorless crystalline solid
2. It is one of the largest constitutions of coal tar.
3. Melting point of naphthalene is 82°C.
4. Boiling point of naphthalene is 218°C.
5. It is the simplest fused ring system.
6. It is insoluble in water but soluble in ether, benzene and hot ethanol.
7. It has a characteristic ‘moth ball’ odor.
Reaction of naphthalene
Naphthalene also gives electrophilic substitution reaction, in this reaction electron attach on two different place and make two different structures.
1. Nitration:- naphthalene undergoing nitration with concentrated nitric acid in the presence of sulphuric acid at 60°C to produce 1- nitronaphthalene.
2. Friedel craft alkylation:- naphthalene undergoes alkylation with alkyl halides in the presence of aluminum chloride to give 2-alkylnaphthalene. (Methyl halides do not react.)

3. Reduction:- naphthalene undergoes reduction more readily than benzene when it reacts with sodium and ethyl alcohol it gives 1,4-dihydronaphthalene.

4. Oxidation:- naphthalene is much more easily oxidized than benzene when it reacts with chromium trioxide in acetic acid at room temperature it gives 1,4-naphthaquinone.

Medicinal uses of naphthalene
1. Naphthalene is used in manufacture of moth balls to protect wooden goods.
2. In the production of pathetic anhydride.
3. In the synthesis of dyes.
4. Used to make plasticizers and natural rubber.
5. Also used in leather industry.
6. Naphthalene is used in production of plastic and bear bottles.
7. Also used in dyes and several medicinal products.
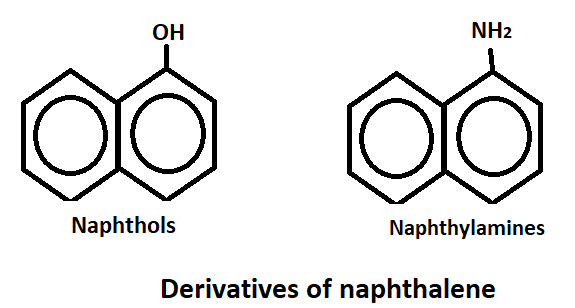
Derivatives of naphthalene
Naphthalene is a hydrocarbon compound which has derivatives that are used in various industries. These derivatives of naphthalene have a wide range of applications, from being used as solvents and insecticides to being used in the production of dyes, plastics and pharmaceuticals. As like, naphthol’s and naphthylamines.
Polynuclear hydrocarbons
Polynuclear hydrocarbons are organic compounds which contain only hydrogen and carbon, which further composed in the form of multiple aromatic rings.
Those compounds in which more than two hydrocarbon aromatic rings are present is called polynuclear hydrocarbons. Eg.- naphthalene, anthracene, phenanthrene…etc


1 thought on “Naphthalene – Structure, Synthesis, Reaction, Physical properties, Medicinal uses, Best notes on naphthalene(1)”